Stone Classification
Stones have been used in building construction since thousands of years. Its qualities like durability, strength, hardness, etc. has made it one of the effective materials for construction purposes.
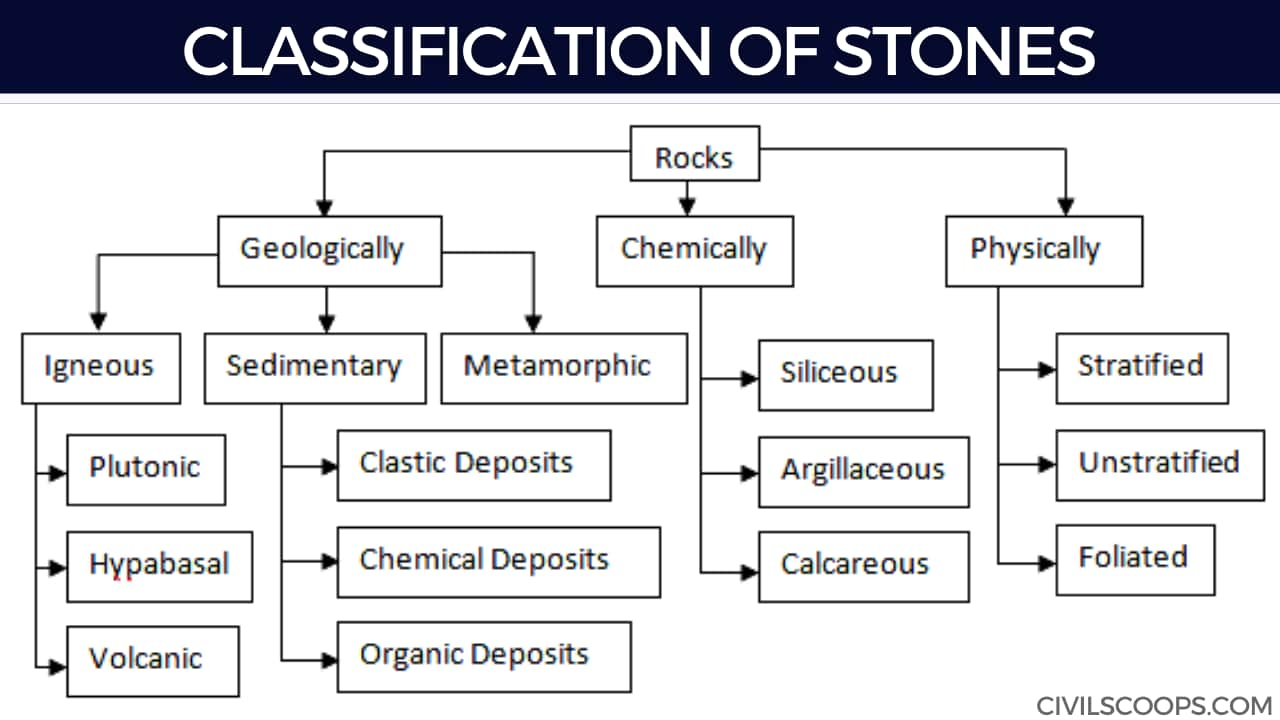
Stones are derived from rocks which are classified as:-
- Geological origin: Sedimentary, Igneous and Metamorphic
- Chemical composition: Siliceous, Argillaceous and Calcareous
- Physical form: stratified, unstratified and foliated
Geological classification of Rocks
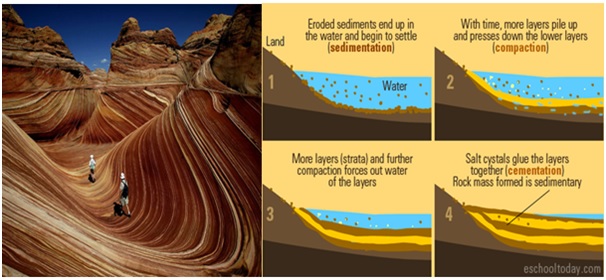
Sedimentary Rocks
They are formed as the sediments deposited over a period of time mostly at the bottom of sea and oceans. They include minerals and remains of plants and animals. E.g. Limestone, Sandstone
Metamorphic Rocks
They are formed when the already existing rocks undergo changes due to intensive heat and pressure. E.g. Marble, Slate

Igneous Rocks
These stones are formed when the molten magma from the earth cools inside the earth or on the earth surface and solidifies. E.g. Granite

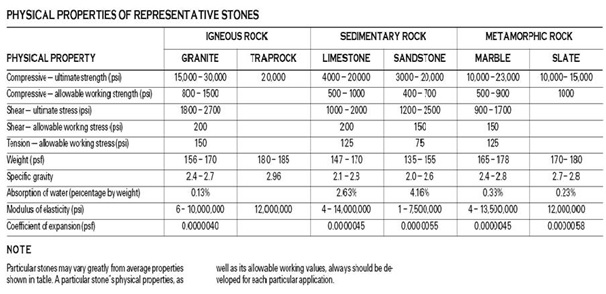
Physical Properties Classification
Chemical classification of Rocks
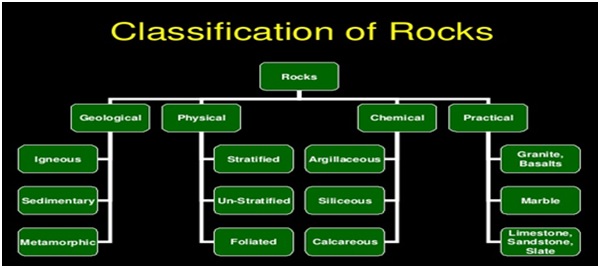
Siliceous Rocks
They are sedimentary rocks which mainly contain silica. They are hard and durable. E.g. Flint, Chert

Argillaceous Rocks
They are sedimentary rocks with the main constituent as argil i.e., clay. These stones arehard and durable but they are brittle. They cannot withstand shock. E.g. Mudstone, Claystone, Slates and laterites.

Calcareous Rocks
They basically are sedimentary rocks with main constituent as calcium carbonate. Limestone is acalcareous rock of sedimentary origin while marble is a calcareous rock of metamorphic origin.

Physical classification of Stones
Stratified
- Stratified rocks show a layered structure and can be easily split up into slabs. Sedimentary rocks are stratified rocks.E.g. sandstone, limestone, slate, etc.
Unstratified
- They cannot be easily split into thin layers. Igneous rocks are unstratified rocks. E.g. Granite, trap, marble, etc.
- Metamorphic rocks may be either stratified or unstratified
Components of Rocks: Crystals and Grains
Crystals
- They are individual minerals that have grown in place to form a rock. In igneous rocks they are minerals that crystallize from the solidifying magma/lava. In metamorphic rocks, they are minerals that grow within the solid rock through chemical reactions between neighbouring minerals. Thus identifying crystals in a rock means that the rock must be either igneous or metamorphic.
Grains
- They are pieces of pre-existing rock or organic material (e.g., shells) that have been cemented together to form a sedimentary rock. Thus identifying grains in a rock means that the rock must be sedimentary.
The list of rocks suitable for building stone is summarized in the table below :-
| Rock Family | Rock Name | Common Colors | Common Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sedimentary | Sandstone | Reddish Brown, Beige, White, Grey | Grainy; composed of rounded grains up to 2 mm in diameter. “Sandy” feel. Bedding is common. |
| Limestone | Grey, Cream, Tan, Pink | Grainy. Fossils are common. Bedding is common. Stylolites are common. | |
| Igneous | Granite | White, Pink, Speckled | Crystalline. Crystals large enough to see. Light colored |
| Granodiorite | “Salt and Pepper” | Crystalline. Crystals large enough to see. Mix of light and dark crystals. | |
| Gabbro | Black, Green, Dark Grey | Crystalline. Crystals large enough to see. Dark colored | |
| Metamorphic | Marble | White, Pink | Crystalline. Wispy, “marbled” textures are common. No fossils. |
| Gneiss | Pink, Black and White | Crystalline. Bands of distinctly different color. Bands may be irregular and folded |
Manufacturing Processes
The process of manufacturing engineered stone can be broken down into:-
- Creating/gathering the material
- Forming the block/slab using industrial machine
- Processing the finished block/slab into tiles or other products
Some companies import boulders themselves to crush into agglomerates (stone powders) of various grain size for their products, others simply buy already crushed stone powders.
After the block / slab is formed and cured (this usually takes between three and seven days depending on products and weather conditions), the stone can be processed in basically the same manner as its natural counterpart.
Detailed manufacturing process includes:
- Selection of the right Quarry and the Big Block
- Cutting down the Block to Slabs
- Sizing of the Slabs
- Filling Process
- Polishing or Honing
- Final Quality Check and Shade Selection
Manufactured Stone
Manufactured Stone is made up of concrete mix which is moulded and colored to give a realistic look and feel of natural stone. They are widely used in home decorations and public buildings.

Advantages
- Manufactured Stones are more lightweightand flat back. This allows for its easy and faster to install as compared to natural stones
- It is reusable, eco-friendly, non-toxic and new green interior decoration material
- Easy to clean
- Heat, fire and Impact resistant
- Repairable and used long term
Disadvantages
- Manufactured stones are costly as compared to readily for freely available natural stones
- To avoid improper installation hiring a professional is a necessity. Flaws in the installation are apparent if not done properly
- They do not give a realistic look like that of natural stones
- Certain limitations like outdoor use/swimming pool as they may get affected by sunlight/chlorine
